CPT (Current Procedural Terminology) codes are standardized codes used to describe medical procedures and services․ They ensure accurate documentation and billing for healthcare providers․
These codes help standardize medical billing, facilitating communication between providers, insurers, and patients․ They also enable tracking of clinical data and quality metrics effectively․
1․1 Definition and Purpose of CPT Codes
CPT (Current Procedural Terminology) codes are standardized codes used to describe medical, surgical, and diagnostic services․ They are maintained by the American Medical Association (AMA) to ensure uniformity in reporting and billing medical procedures․
The primary purpose of CPT codes is to provide a consistent and standardized way to describe medical services, facilitating accurate billing, insurance claims, and data collection․ They are essential for healthcare providers, insurers, and patients to communicate effectively about the services rendered․
For procedures like ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsy, CPT codes help in identifying the specific services performed, such as imaging guidance or tissue sampling, ensuring precise documentation and reimbursement․
These codes are regularly updated to reflect advancements in medical practices and technologies, ensuring they remain relevant and comprehensive for modern healthcare needs․
1․2 Importance of CPT Codes in Medical Billing
CPT codes are crucial in medical billing as they provide a standardized method for reporting medical procedures and services․ They ensure accurate and consistent billing, facilitating seamless communication between healthcare providers and insurers․
By using specific codes, practices can document procedures like ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsies precisely, minimizing billing errors and ensuring proper reimbursement․ CPT codes also help track patient data and monitor healthcare trends effectively․
Accurate coding supports compliance with regulatory requirements, reduces audit risks, and improves operational efficiency in medical billing․ This standardized system is essential for maintaining transparency and fairness in healthcare billing processes․

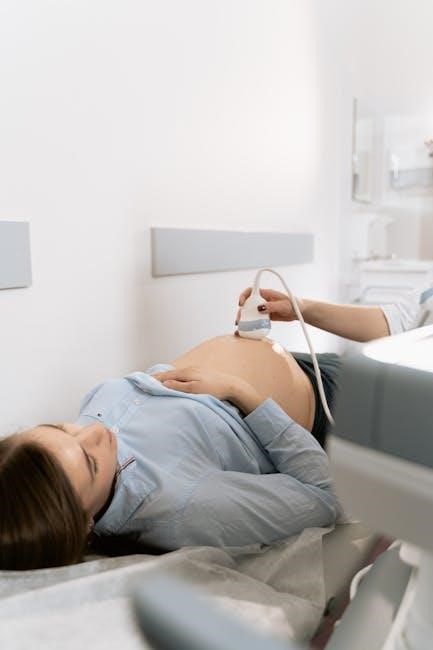
Overview of Ultrasound-Guided Thyroid Biopsy
Ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsy is a minimally invasive procedure using sound waves to locate thyroid nodules for tissue sampling․ It ensures precise needle placement and accurate diagnosis․
2․1 What is an Ultrasound-Guided Thyroid Biopsy?
An ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsy is a minimally invasive procedure where ultrasound technology is used to guide a needle to thyroid nodules for tissue sampling․
It allows real-time imaging to ensure precise needle placement, reducing risks and improving diagnostic accuracy․ This method is particularly useful for evaluating suspicious thyroid lesions․
The procedure is typically performed under local anesthesia, with the ultrasound machine providing clear visualization of the nodule and surrounding structures․
By combining imaging guidance with fine-needle aspiration, it enables healthcare providers to collect tissue samples for cytological examination, aiding in the diagnosis of thyroid conditions․
This approach minimizes complications and enhances the effectiveness of thyroid nodule evaluation, making it a preferred diagnostic tool in clinical practice․
2․2 Clinical Significance of the Procedure
Ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsy is crucial for diagnosing thyroid nodules, ensuring accurate tissue sampling for cytological evaluation․
It helps differentiate benign from malignant lesions, guiding treatment decisions and avoiding unnecessary surgeries․
The procedure’s precision reduces complications like bleeding or infection, making it safer for patients․
By enabling early detection of thyroid cancer, it improves patient outcomes and prognosis․
Regular use of this procedure aligns with clinical guidelines, emphasizing its role in modern thyroid care․
2․3 Common Indications for the Procedure
Ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsy is typically indicated for evaluating thyroid nodules suspected of being malignant․
Nodules with suspicious ultrasound features, such as irregular margins or increased vascularity, often require biopsy․
Patients with a history of thyroid cancer or radiation exposure may also benefit from this procedure․
Additionally, nodules that exhibit significant growth over time or cause symptoms like neck swelling warrant further investigation;
The procedure is particularly useful for nodules larger than 10 mm, as smaller ones may not require immediate intervention unless clinical suspicion is high․
It serves as a diagnostic tool to differentiate between benign and malignant lesions, guiding appropriate management strategies․

CPT Codes for Ultrasound-Guided Thyroid Biopsy
CPT codes are essential for standardized documentation and billing of medical procedures, ensuring accurate reimbursement and compliance with coding guidelines․
3․1 Primary CPT Code for the Procedure
The primary CPT code for an ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsy is 10005, which represents the fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy of the first thyroid nodule․ This code is used when imaging guidance, such as ultrasound, is utilized to locate the nodule and guide the needle placement․ It is essential to report this code for the initial lesion sampled․ If multiple nodules are biopsied, additional codes such as 10006 may apply․ Proper coding ensures accurate billing and reimbursement for the procedure․
3․2 Additional CPT Codes for Multiple Lesions
For ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsies involving multiple nodules, an additional CPT code, 10006, is used to report each extra lesion sampled beyond the first․ This code applies when more than one nodule requires fine needle aspiration (FNA) during the same procedure․ It is essential to use 10006 for each subsequent lesion to ensure accurate billing․ If ultrasound guidance is utilized for each additional lesion, 76942 should also be reported for the imaging component․ Proper coding for multiple lesions ensures correct reimbursement and reflects the complexity of the procedure accurately․
3․3 Coding for Ultrasound Guidance
When ultrasound guidance is used during a thyroid biopsy, the procedure involves the use of specific CPT codes to account for the imaging component․ The primary code for the biopsy itself is 10005 for the first nodule, and 10006 for each additional nodule․ However, the ultrasound guidance is separately reported using the code 76942․ This code is essential for capturing the technical aspect of using ultrasound to guide the needle placement․ Proper documentation of the imaging guidance ensures accurate billing and reflects the use of advanced imaging techniques in the procedure․ It is important to include 76942 to avoid undercoding and ensure the practice receives appropriate reimbursement for the service provided․ This code is typically billed once per session, regardless of the number of nodules sampled․ Proper coding practices dictate that 76942 should accompany 10005 or 10006 when ultrasound guidance is utilized․ Ensuring these codes are correctly paired is crucial for compliance with billing guidelines and to prevent any potential issues with insurance claims․ By including 76942, practices can demonstrate the use of precise imaging techniques, which are vital for accurate biopsy outcomes․ Additionally, this code highlights the importance of ultrasound in minimizing complications and improving the efficacy of the procedure․ Accurate reporting of 76942 ensures that the practice is fairly compensated for the technical skills and resources required to perform ultrasound-guided biopsies․ Therefore, careful attention to coding for ultrasound guidance is essential in the billing process for thyroid biopsies․
Specific CPT Codes
The primary CPT codes for ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsy include 10005 for the first nodule and 10006 for each additional nodule․ 76942 is used for ultrasound guidance․
4․1 CPT Code 10005: First Nodule Sampling
CPT code 10005 is used for the initial sampling of the first thyroid nodule during an ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy․ This code represents the primary procedure․
It applies to the first nodule sampled and includes imaging guidance․ For example, if a patient has multiple nodules, 10005 is used once for the first nodule․
Each additional nodule requires a separate code, typically 10006․ Accurate coding ensures proper billing and reimbursement for the procedure․
For instance, if both the right and left thyroid nodules are sampled, 10005 would be used for the first nodule, and 10006 for the second․
This distinction is critical to avoid coding errors and ensure compliance with billing guidelines․
4․2 CPT Code 10006: Each Additional Nodule
CPT code 10006 is used to report each additional thyroid nodule sampled during an ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration biopsy, beyond the first nodule․
This code is an add-on to the primary procedure code 10005, which covers the first nodule․ For example, if three nodules are sampled, 10005 is used once, and 10006 is used twice․
It is essential to bill 10006 separately for each additional nodule to ensure accurate reimbursement․ This code reflects the incremental work involved in sampling multiple lesions․
Proper use of 10006 avoids undercoding and ensures compliance with billing guidelines for multiple nodule biopsies․ Always pair it with 10005 for the first nodule․
4․3 CPT Code 76942: Ultrasound Guidance
CPT code 76942 is used to report ultrasound guidance for needle placement during procedures like thyroid biopsies․ This code is billed separately from the biopsy procedure itself․
It applies to each distinct lesion requiring ultrasound guidance, ensuring accurate needle placement․ For multiple nodules, 76942 is billed once per lesion, reflecting the additional time and skill required․
Proper documentation is essential to justify its use․ Always pair 76942 with the primary biopsy code (e․g․, 10005 or 10006) for complete reporting․ This ensures proper reimbursement and compliance with coding guidelines․

Billing and Coding Guidelines
Accurate coding ensures proper reimbursement․ Adhere to guidelines for CPT codes, documentation, and sequencing to avoid errors․ Proper billing reflects the procedure’s complexity and ensures compliance with payer policies․
5․1 General Coding Guidelines
When coding for an ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsy, ensure accuracy by selecting the appropriate CPT codes․ Use 10005 for the first nodule sampled and 10006 for each additional nodule․ Always report 76942 for ultrasound guidance․
Verify documentation for procedure details, including imaging guidance and the number of nodules sampled․ Ensure compliance with payer-specific rules and updates in coding guidelines to avoid denials․
Documentation must clearly state the use of ultrasound guidance and the number of nodules biopsied․ Accurate coding ensures proper reimbursement and reflects the procedure’s complexity․
5․2 Specific Guidelines for Multiple Lesions
For ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsies involving multiple lesions, use CPT code 10006 for each additional nodule after the first․ The primary lesion is coded with 10005․ Ensure 76942 is reported for ultrasound guidance for each lesion requiring separate needle placement․
Document the number of nodules sampled and their locations․ Accurate coding prevents billing errors and ensures proper reimbursement․ Always verify payer-specific guidelines for multiple lesion procedures to avoid claim denials․
Remember, each additional nodule beyond the first requires a separate 10006 code․ This ensures precise billing for the procedure’s complexity and resources used․
5․3 Documentation Requirements
Accurate documentation is critical for proper coding and billing of ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsies․ Ensure the medical record includes details of the procedure, such as the number of nodules sampled and the use of ultrasound guidance․
Document the CPT codes used, including 10005 for the first nodule and 10006 for each additional lesion․ Also, note the use of 76942 for ultrasound guidance․ Include pre-procedure and post-procedure notes, imaging results, and pathology reports․
Maintain records of patient consent, medical necessity, and clinical rationale for the biopsy․ Proper documentation ensures compliance with coding guidelines and supports accurate reimbursement․ Always retain records for auditing purposes․

Clinical Indications and Guidelines
Ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsy is recommended for nodules meeting specific size criteria or exhibiting suspicious features․ It aids in evaluating thyroid abnormalities and diagnosing conditions accurately․
6․1 When is an Ultrasound-Guided Thyroid Biopsy Recommended?
An ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsy is typically recommended for nodules meeting specific size criteria or exhibiting suspicious features on imaging․ Nodules larger than 10 mm, especially with concerning characteristics like irregular borders or microcalcifications, often warrant a biopsy․ Symptomatic nodules causing difficulty swallowing, breathing, or voice changes may also prompt a biopsy․ Additionally, growing nodules or those with a concerning patient history, such as prior radiation exposure, are evaluated․ Guidelines from organizations like the American Thyroid Association help standardize these recommendations, ensuring timely and accurate diagnosis of thyroid abnormalities․
6․2 Role of Ultrasound in Thyroid Nodule Evaluation
Ultrasound plays a critical role in evaluating thyroid nodules by providing detailed imaging of the thyroid gland․ It helps identify the size, composition, and suspicious features of nodules, such as solid vs․ cystic components, irregular margins, or microcalcifications․ Ultrasound is non-invasive and uses sound waves to produce high-resolution images, making it the preferred imaging modality for thyroid assessment․ It is essential for guiding fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsies, ensuring accurate tissue sampling․ Additionally, ultrasound monitors nodule growth over time, aiding in early detection of potential malignancies․ This imaging technique is vital for both diagnostic and procedural purposes in thyroid nodule management․
6․3 Guidelines for Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA)
Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA) is a diagnostic procedure for evaluating thyroid nodules, often performed under ultrasound guidance․ Guidelines recommend FNA for nodules larger than 10 mm or smaller nodules with suspicious ultrasound features, such as irregular margins or microcalcifications․ The procedure involves using a thin needle to collect tissue samples for cytological examination․ Clinical judgment is crucial in determining when FNA is appropriate, as not all nodules require biopsy․ The American Thyroid Association and other organizations provide detailed criteria to guide decision-making; Proper technique and adherence to guidelines ensure accurate diagnosis and minimize complications․ CPT codes 10005 and 10006 are used for coding FNA procedures, with 76942 for ultrasound guidance․
Insurance Coverage and Reimbursement
Insurance coverage for ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsy varies by provider, but most plans cover medically necessary procedures․ Accurate CPT coding ensures proper reimbursement for the procedure and imaging guidance․
7․1 Insurance Coverage for the Procedure
Insurance coverage for ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsy is typically available under most health plans when deemed medically necessary․ Providers often cover this procedure to diagnose thyroid nodules or abnormalities․ However, coverage details may vary depending on the insurer and specific policy terms․ Patients should verify their plan’s benefits to understand any out-of-pocket costs or pre-authorization requirements․ Proper documentation and accurate CPT coding, such as 10005 and 76942, are essential for seamless reimbursement․ It’s also important for providers to ensure that the procedure meets clinical guidelines for coverage eligibility, reducing the risk of denied claims․
7․2 Reimbursement Rates and Considerations
Reimbursement rates for ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsy vary by payer and policy․ Medicare and private insurers typically reimburse procedures when deemed medically necessary․ The specific CPT codes used, such as 10005 for the first nodule and 76942 for ultrasound guidance, influence reimbursement amounts․ Accurate coding and documentation are critical to ensure proper payment․ Reimbursement rates may also depend on the healthcare setting, with hospital-based procedures often reimbursed differently than outpatient services․ Providers should consult payer guidelines and fee schedules to understand expected payments․ Additionally, regional variations and updates to payment policies can affect reimbursement rates, making it essential to stay informed about current coding and billing practices․
7․3 Coding for Reimbursement Accuracy
Accurate coding is essential for proper reimbursement in ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsy procedures․ Using the correct CPT codes, such as 10005 for the first nodule and 10006 for additional nodules, ensures precise billing․ The code 76942 should also be included for ultrasound guidance․ Proper documentation of medical necessity and the procedure’s details is critical to avoid reimbursement delays or denials․ Payers often require clear justification for multiple lesions or additional imaging guidance․ Coding errors, such as missing or incorrect modifiers, can lead to reduced or denied payments․ Regular updates to coding guidelines and payer policies must be monitored to maintain compliance and ensure accurate reimbursement․

Potential Coding Errors and Pitfalls
Common coding errors include missing codes for additional nodules and failure to include modifiers․ Using incorrect codes can lead to claim denials and delays․
8․1 Common Mistakes in Coding
- Not coding for additional nodules: Failing to report subsequent lesions with CPT code 10006 can result in underpayment․
- Omitting ultrasound guidance: Forgetting to include CPT code 76942 for imaging guidance can lead to denied claims․
- Incorrect use of modifiers: Not applying appropriate modifiers for multiple procedures can cause billing errors․
- Not documenting multiple lesions: Missing documentation for separate nodules may prevent accurate coding for additional biopsy samples․
These errors highlight the need for meticulous coding practices to ensure proper reimbursement and compliance with guidelines․
8․2 Consequences of Incorrect Coding
Incorrect coding for ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsy can lead to denied claims, delaying payments and requiring resubmission․ This may result in financial losses for healthcare providers due to unpaid services․ Additionally, audits by insurance companies or regulatory bodies may uncover coding errors, potentially leading to penalties or legal actions․ Inaccurate coding can also affect patient trust and satisfaction, as they may face unexpected medical bills․ Furthermore, repeated errors can damage a provider’s reputation and lead to loss of reimbursement․ Accurate coding is essential to avoid these consequences and ensure compliance with healthcare regulations․ Proper documentation and coding practices are critical to maintaining financial and operational integrity․
8․3 Best Practices to Avoid Errors
To prevent coding errors for ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsies, adhere to established guidelines and use current CPT code updates․ Ensure thorough documentation of procedures, including imaging guidance and any additional lesions․ Use specific codes for each service, such as 76942 for ultrasound guidance and 10005 for the first nodule․ Regularly train staff on coding updates and conduct internal audits to identify and correct errors․ Leveraging coding software can also help automate checks and reduce human error․ Clear communication between clinical and billing teams is crucial for accurate claim submissions․ By following these practices, healthcare providers can minimize errors and ensure compliant reimbursement․ Consistency and attention to detail are key to avoiding costly mistakes․

Complications and Risks
Complications of ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsy may include bleeding, infection, or thyroid damage․ Proper technique and post-procedure care minimize these risks, ensuring patient safety and optimal outcomes․
9․1 Potential Complications of the Procedure
Ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsy is generally safe but may have complications․ Common risks include bleeding, infection, or bruising at the biopsy site․ Rarely, hematoma or thyroid gland damage can occur․ Proper technique minimizes these risks․
9․2 Coding for Complications
When complications arise, specific CPT codes are used for reporting․ For example, hematoma treatment may involve codes like 20526 for drainage or 76942 for ultrasound-guided hematoma aspiration․ Infection-related complications could require 10022 for incision and drainage․ Additionally, any imaging or follow-up procedures would need their respective codes․ It is crucial to document the complication and its treatment accurately to ensure proper coding and reimbursement․ Always refer to the latest CPT guidelines to confirm the appropriate codes for each scenario․
9․3 Risk Factors and Contraindications
Understanding risk factors and contraindications is crucial for safe ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsy․ Bleeding disorders or anticoagulant use increase bleeding risks․ Pregnancy requires cautious evaluation due to potential risks․ Severe coagulopathy or uncontrolled bleeding disorders are contraindications․ Infections or severe thyroid disease may also pose risks․ Proper patient evaluation and consultation with specialists are essential to minimize complications and ensure safe outcomes․
CPT codes are essential for accurate billing and documentation of ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsy․ Proper coding ensures reimbursement and reflects high-quality patient care and procedural precision․
10․1 Summary of Key Points
The use of CPT codes for ultrasound-guided thyroid biopsy ensures accurate billing and documentation․ Key codes include 10005 for the first nodule and 10006 for additional nodules, with 76942 for ultrasound guidance․ Proper coding is essential for reimbursement and compliance with medical billing standards․ Accurate documentation of the procedure and any complications is critical for avoiding coding errors․ Understanding these codes helps healthcare providers maintain efficient and precise billing processes․ This ensures seamless communication between providers, insurers, and patients․ By adhering to coding guidelines, practices can avoid disputes and ensure fair reimbursement for services rendered․
10․2 Importance of Accurate Coding
Accurate coding is essential for ensuring proper reimbursement, avoiding claim denials, and maintaining compliance with regulatory standards․ Correct use of CPT codes like 10005 and 76942 ensures that healthcare providers are fairly compensated for their services․ Inaccurate coding can lead to financial losses, audits, and legal issues․ It also ensures transparency and trust with patients, who rely on clear and justified billing․ By adhering to coding guidelines, practices can optimize their revenue cycle and maintain operational efficiency․ Accurate coding also supports data integrity, enabling better tracking of clinical outcomes and resource allocation․ It is a cornerstone of ethical and efficient healthcare administration․
10․3 Future Directions in Coding Practices
Future coding practices will focus on precision and integration of advanced technologies․ CPT codes will likely undergo updates to reflect new procedures and imaging techniques, ensuring accurate billing․ The use of AI and machine learning may automate code selection, reducing errors․ Enhanced specificity in codes will improve data tracking and outcomes analysis․ Regular updates to guidelines and training programs will be essential for coders to stay informed․ These advancements aim to streamline workflows, reduce discrepancies, and enhance compliance․ By embracing these changes, healthcare providers can ensure accurate reimbursement and maintain high standards of patient care, making coding practices more efficient and reliable in the years to come․






